Unit 1: Biochemistry
Vocab:
Matter = Anything that takes up space and has mass.
Element = Substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by chemical reactions.
Essential element = Elements required for an organism to live and reproduce. Hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, nitrogen are the main essential elements. There are also some trace elements.
Compound = substance consisting of 2 or more different elements.
Molecule = substance consisting of 2 or more elements. Not necessarily different.
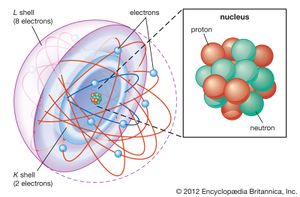
Atom = Smallest unit of matter. Still retains the properties of an element.
Subatomic particles = two nuclear subatomic particles: Proton (+tive charge) and neutrons (no charge); and 1 orbiting subatomic particle: Electron (-tive charge).
atomic number= number of protons.
atomic mass= Average weight of number of protons plus neutrons.
isotope= Different atomic forms of the same element (different number of neutrons).
Valance shell= outer shell of electrons. Bonding part of an atom. Either 2 (first) or 8 (all others) electrons.
Chemical bond= sharing or taking of electrons.
covalent bond= sharing a pair of two valence electrons by two atoms. It is the strongest bond.
Ionic bond= Atom taking an electron from another atom. Forms between a cation and a anion. Weak bond in aqueous solutions.
Electronegativity = The power of an atom to attract electrons to itself.
Non polar bond= Electrons are shared equally.
Polar bond= Electrons are not shared equally.
Anion= negative ion.
Cation= positive ion.
Hydrogen bond= Bond between hydrogen and an electronegative atom. See high specific heat.
Acid= Substance that increases the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution.
Base= Substance that reduces the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution.
Molecular mass= the molecular mass of a molecule is equal to the sum of the atomic masses of it's elements.
Avogadro's number= 6.02*10^23
Molar mass= a molecule's molar mass is equal to the molecule's molecular mass number in grams. This is called 1 mole. It is also equal in mass to an Avogadro's number amount of the molecule.
Organic chemistry = Study of compounds containing carbon.
Hydrocarbon= Molecule of only hydrogen and carbon.
Macromolecule= Very large molecule. These include carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids.
Polymer= Long molecule consisting of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds.
Monomer= The similar or identical building block used in a polymer.
Enzyme= Specialised macromolecules that speed up chemical reactions.
Lipid= Not soluble in water. Most common types are fats, phospholipids, and steroids.
Fat= Large molecules assembled from smaller molecules by dehydration reactions.
Fatty acids= Long carbon skeleton and a carboxyl group.
Triacylglycerol= 3 fatty acids, and one glycerol molecule.
Phospholipid= 2 fatty acids and glycerol and a phosphate group.
Steroids= Lipids characterised by a carbon skeleton consisting of four fused rings
Catalyst= Something that starts or speeds up a chemical reaction without being consumed.
Amino Acids= Building blocks of proteins. Made up of an amino group, and a carboxyl group.
Peptide bond= Bond between 2 amino acids.
Polypeptide= Polymer of amino acids.
Protein= One or more connected polypeptides.
Nucleic acid= Polymer made of nucleotides. The two types are DNA and RNA.
DNA= Provides instruction for protein synthesis.
Nucleotide= Sugar, phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
Nucleoside= Sugar, and a nitrogenous base.
Nitrogenous base= A nitrogenous base for DNA can be: Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, or Cytosine. For RNA it can be Adenine, Uracil, Guanine, and Cytosine.