Unit 3: Genetics
Meiosis and sexual Life Cycles
Genes: Genetic code inherited from parents that determines an organism's traits.
Asexual reproduction: When an organism is the only parent and passes its genes to an offspring without the use of any gametes.
Sexual reproduction: When an offspring is given a unique mix of genes from two parents.
Clone: Offspring produce in asexual reproduction.
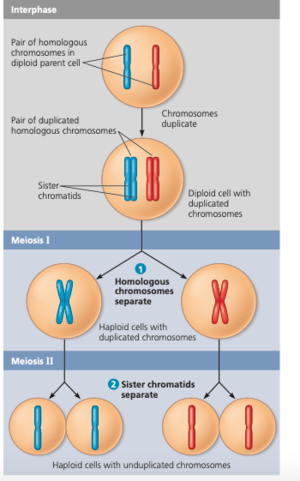
Chromosome: Every somatic cell has chromosomes dictating certain properties. Chromosomes come in 23 sets of 2 in humans.
Haploid cell: Cell the contains a single set of chromosomes.
Diploid cell: Cell that contains two sets of chromosomes.
Triploid cell: Cell that contains three sets of chromosomes.
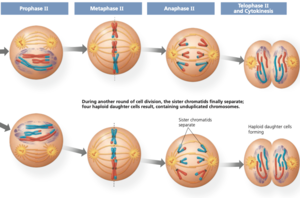
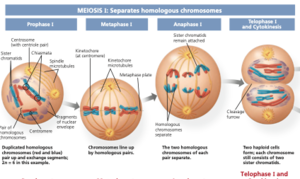
Meiosis: Meiosis separates one diploid cell into four haploid cells. It has phases: Prophase I, Pro-metaphase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase I, Prophase II, Pro-metaphase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, and Telophase II. In prophase I the two chromosomes mix and intangible with each other. The remaining phases are all pretty similar to their mitosis counterpart with the same name.
Allele: Variant of a gene. You get one from each of your parents for every gene.
Phenotype: Observable effects of an individual's genotype. Dictated by their alleles.
Homozygous: A homozygous gene is a gene with two of the same alleles.
Heterozygous: A heterozygous gene is a gene with two different alleles.
Dominant allele: A heterozygous gene will adopt this allele's trait.
Recessive allele: A heterozygous gene will not adopt this allele's trait. A recessive allele can only effect an organism by being part of a homozygous gene.
Pedigree: Record of a certain gene in a family.
Genetic disorder: Disease inherited from parents. Usually (but not always) in the form of a recessive allele.
Carrier: Homozygous organism with one recessive allele of a genetic disorder. The carrier usually won't be affected by the disorder themselves, but if mating with another carrier, can potentially give the disorder to their offspring.
Epistatis: When a second gene's presence will affect a different gene.
Wild type: The most commonly appearing allele of a gene.
Sex linked genes: Genes that are located exclusively on either the x or y chromosome. Called x-linked and y-linked genes respectively.
X linked genes: X linked recessive alleles can be passed down to family members of both sexes, but will only affect males.
Parental type: Same allele as a parent.
Recombinant type: different allele to both parents.