Difference between revisions of "Unit 1: Biochemistry"
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | == Elements == | |
| − | |||
Matter = Anything that takes up space and has mass. | Matter = Anything that takes up space and has mass. | ||
Element = Substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by chemical reactions. | Element = Substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by chemical reactions. | ||
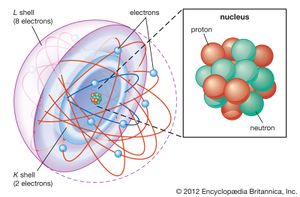
| − | Essential element = Elements required for an organism to live and reproduce. Hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, nitrogen are the main essential elements. There are also some trace elements. | + | Essential element = Elements required for an organism to live and reproduce. Hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, nitrogen are the main essential elements. There are also some trace elements.[[File:Shell-atomic-model-shell-shells-electrons-energy.jpg|thumb|Atom diagram]] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[File:Shell-atomic-model-shell-shells-electrons-energy.jpg|thumb|Atom diagram]] | ||
Atom = Smallest unit of matter. Still retains the properties of an element. | Atom = Smallest unit of matter. Still retains the properties of an element. | ||
| Line 39: | Line 33: | ||
Cation= positive ion. | Cation= positive ion. | ||
| − | Hydrogen bond= Bond between hydrogen and an electronegative atom. See [[Water|high specific heat]]. | + | Hydrogen bond= Bond between hydrogen and an electronegative atom. See [[Water|high specific heat]]. |
Acid= Substance that '''increases''' the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution. | Acid= Substance that '''increases''' the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution. | ||
Base= Substance that '''reduces''' the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution. | Base= Substance that '''reduces''' the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Molecules == | ||
| + | Molecule = substance consisting of 2 or more elements. Not necessarily different. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Compound = substance consisting of 2 or more '''different''' elements. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Hydrocarbon= Molecule of only hydrogen and carbon. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Macromolecule= Very large molecule. These include [[carbohydrates]], proteins, and nucleic acids. '''YOU CAN REMOVE THE LINK LEADING TO AN EMPTY PAGE. Douglas: same as the one on high specific heat, this link works for me.''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Polymer= Long molecule consisting of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Monomer= The similar or identical building block used in a polymer. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Enzyme= Protein that is a catalyst. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Image 2020-12-22 124116.png|thumb|Protein Structures]] | ||
| + | Catalyst= Something that starts or speeds up a chemical reaction without being consumed. | ||
| + | [[File:Amino Acid Structure.jpg|thumb]] | ||
| + | Amino Acids= Building blocks of proteins. Made up of an amino group, and a carboxyl group..... | ||
| + | |||
| + | Peptide bond= Bond between 2 amino acids. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Polypeptide= Polymer of amino acids. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Protein= One or more connected polypeptides. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''THE SEPARATION YOU HAVE FOR NUCLEIC ACIDS IS USEFUL. PLEASE DO THE SAME FOR LIPIDS, PROTEINS, AND CARBOHYDRATES. Douglas: I made a section for lipids. But there is already a separate page for carbohydrates.''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Nucleic acids == | ||
| + | Nucleic acid= Polymer made of nucleotides. The two types are DNA and RNA. | ||
| + | |||
| + | DNA= Provides instruction for protein synthesis. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Nucleotide= Sugar, phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Nucleoside= Sugar, and a nitrogenous base. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Nitrogenous base= A nitrogenous base for DNA can be: Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, or Cytosine. For RNA it can be Adenine, Uracil, Guanine, and Cytosine. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Lipids == | ||
| + | Lipid= Not soluble in water. Most common types are fats, phospholipids, and steroids. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Fatty acids= Long carbon skeleton and a carboxyl group. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Fat= Large molecules assembled from fatty acids by dehydration reactions. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Triacylglycerol= 3 fatty acids, and one glycerol molecule. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Phospholipid= 2 fatty acids and glycerol and a phosphate group. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Steroids= Lipids characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of four fused rings. | ||
Latest revision as of 07:43, 4 January 2021
Elements
Matter = Anything that takes up space and has mass.
Element = Substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by chemical reactions.
Essential element = Elements required for an organism to live and reproduce. Hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, nitrogen are the main essential elements. There are also some trace elements.
Atom = Smallest unit of matter. Still retains the properties of an element.
Subatomic particles = two nuclear subatomic particles: Proton (+tive charge) and neutrons (no charge); and 1 orbiting subatomic particle: Electron (-tive charge).
atomic number= number of protons.
atomic mass= Average weight of number of protons plus neutrons.
isotope= Different atomic forms of the same element (different number of neutrons).
Valance shell= outer shell of electrons. Bonding part of an atom. Either 2 (first) or 8 (all others) electrons.
Chemical bond= sharing or taking of electrons.
covalent bond= sharing a pair of two valence electrons by two atoms. It is the strongest bond.
Ionic bond= Atom taking an electron from another atom. Forms between a cation and a anion. Weak bond in aqueous solutions.
Electronegativity = The power of an atom to attract electrons to itself.
Non polar bond= Electrons are shared equally.
Polar bond= Electrons are not shared equally.
Anion= negative ion.
Cation= positive ion.
Hydrogen bond= Bond between hydrogen and an electronegative atom. See high specific heat.
Acid= Substance that increases the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution.
Base= Substance that reduces the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution.
Molecules
Molecule = substance consisting of 2 or more elements. Not necessarily different.
Compound = substance consisting of 2 or more different elements.
Hydrocarbon= Molecule of only hydrogen and carbon.
Macromolecule= Very large molecule. These include carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids. YOU CAN REMOVE THE LINK LEADING TO AN EMPTY PAGE. Douglas: same as the one on high specific heat, this link works for me.
Polymer= Long molecule consisting of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds.
Monomer= The similar or identical building block used in a polymer.
Enzyme= Protein that is a catalyst.
Catalyst= Something that starts or speeds up a chemical reaction without being consumed.
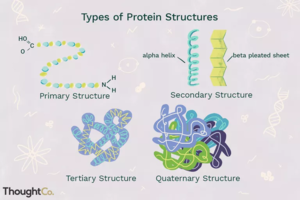
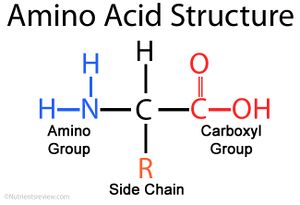
Amino Acids= Building blocks of proteins. Made up of an amino group, and a carboxyl group.....
Peptide bond= Bond between 2 amino acids.
Polypeptide= Polymer of amino acids.
Protein= One or more connected polypeptides.
THE SEPARATION YOU HAVE FOR NUCLEIC ACIDS IS USEFUL. PLEASE DO THE SAME FOR LIPIDS, PROTEINS, AND CARBOHYDRATES. Douglas: I made a section for lipids. But there is already a separate page for carbohydrates.
Nucleic acids
Nucleic acid= Polymer made of nucleotides. The two types are DNA and RNA.
DNA= Provides instruction for protein synthesis.
Nucleotide= Sugar, phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
Nucleoside= Sugar, and a nitrogenous base.
Nitrogenous base= A nitrogenous base for DNA can be: Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, or Cytosine. For RNA it can be Adenine, Uracil, Guanine, and Cytosine.
Lipids
Lipid= Not soluble in water. Most common types are fats, phospholipids, and steroids.
Fatty acids= Long carbon skeleton and a carboxyl group.
Fat= Large molecules assembled from fatty acids by dehydration reactions.
Triacylglycerol= 3 fatty acids, and one glycerol molecule.
Phospholipid= 2 fatty acids and glycerol and a phosphate group.
Steroids= Lipids characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of four fused rings.