Difference between revisions of "Unit 3: Genetics"
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 122: | Line 122: | ||
Mutagen: Substance that increases the odds of mutation. | Mutagen: Substance that increases the odds of mutation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Chapter 18 == | ||
| + | Bacteria: A type of single-celled prokaryotic organisms. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Operon: The operator, promoter and related genes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Regulatory Gene: Gene that encodes for a repressor protein. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Epigenetic inheritance: Inheritance of traits transmitted by mechanisms outside of the nucleotide sequence. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Homeotic genes: regulatory genes that control pattern formation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Chapter 19 == | ||
| + | Capsid: Protein shell enclosing the viral DNA. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Bacteriophage: Virus that infects bacteria. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lytic cycle: Virus replication cycle that requires the death of the host. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Virulent phage : Phage that replicates only by the lytic cycle. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lysogenic cycle: Virus replication cycle that does not require the death of the host. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Temperate phage: Phage capable of lytic and lysogenic cycles. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Restrictive enzymes: Enzymes in bacteria that restrict virus replication. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Viral envelope: Protective shell used by viruses to enter a host cell. | ||
Latest revision as of 07:00, 24 May 2021
Chapter 13
Genes: Genetic code inherited from parents that determines an organism's traits.
Asexual reproduction: When an organism is the only parent and passes its genes to an offspring without the use of any gametes.
Sexual reproduction: When an offspring is given a unique mix of genes from two parents.
Clone: Offspring produce in asexual reproduction.
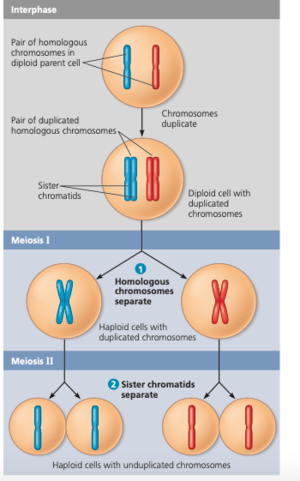
Chromosome: Every somatic cell has chromosomes dictating certain properties. Chromosomes come in 23 sets of 2 in humans.
Haploid cell: Cell the contains a single set of chromosomes.
Diploid cell: Cell that contains two sets of chromosomes.
Triploid cell: Cell that contains three sets of chromosomes.
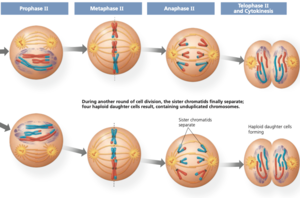
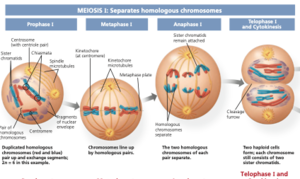
Meiosis: Meiosis separates one diploid cell into four haploid cells. It has phases: Prophase I, Pro-metaphase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase I, Prophase II, Pro-metaphase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, and Telophase II. In prophase I the two chromosomes mix and intangible with each other. The remaining phases are all pretty similar to their mitosis counterpart with the same name.
Allele: Variant of a gene. You get one from each of your parents for every gene.
Phenotype: Observable effects of an individual's genotype. Dictated by their alleles.
Chapter 14
Homozygous: A homozygous gene is a gene with two of the same alleles.
Heterozygous: A heterozygous gene is a gene with two different alleles.
Dominant allele: A heterozygous gene will adopt this allele's trait.
Recessive allele: A heterozygous gene will not adopt this allele's trait. A recessive allele can only effect an organism by being part of a homozygous gene.
Pedigree: Record of a certain gene in a family.
Genetic disorder: Disease inherited from parents. Usually (but not always) in the form of a recessive allele.
Carrier: Homozygous organism with one recessive allele of a genetic disorder. The carrier usually won't be affected by the disorder themselves, but if mating with another carrier, can potentially give the disorder to their offspring.
Epistatis: When a second gene's presence will affect a different gene.
Chapter 15
Wild type: The most commonly appearing allele of a gene.
Mutant type: The non-wild type allele.
Sex linked genes: Genes that are located exclusively on either the x or y chromosome. Called x-linked and y-linked genes respectively.
X linked genes: X linked recessive alleles can be passed down to family members of both sexes, but will only affect males.
Parental type: Same allele as a parent.
Recombinant type: different allele to both parents.
Chapter 16
Origin of replication: Site where DNA replication begins.
Replication bubble: Opening(s) created between the two strands of DNA. There is only one in the circular bacteria DNA. But in eukaryotic DNA, there can be hundreds.
Replication fork: Ends of the replication bubble.
Primer: RNA sequence created at the start of DNA replication, for polymerases to have something to add onto.
DNA polymerase: Enzymes that add new nucleotides to the 3' end of the DNA strand.
Leading strand: A strand of DNA being synthesised from the origin, in a 5' to 3' direction.
Lagging Strand: A strand separated into Okazaki fragments, synthesised towards the origin, in a 5' to 3' direction.
Helicase: Unwinds the double helix at the replication fork.
Single strand binding protein: Stabilises DNA strands by binding to them.
Topoisomerase: Relieves strain on the replication fork.
Primase: Creates the RNA primer.
DNA pol III: DNA polymerase that synthesises new nucleotides to the strand.
DNA pol I: DNA polymerase that removes and replaces the primer with nucleotides.
Ligase: Joins Okazaki fragments. Also connects the primer replacement to the rest of the strand.
Histones: Proteins that help keep DNA contained by allowing it to wrap around them.
Chapter 17
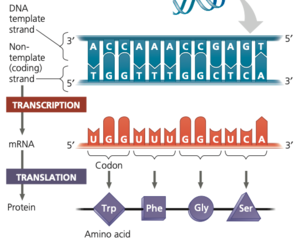
Transcription: The synthesising of mRNA, based on a template DNA strand.
Translation: The synthesising of proteins, based on an mRNA strand.
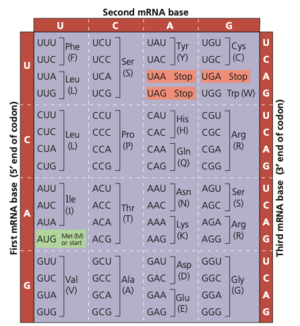
Codon: Group of three adjacent nucleotides that are used to code for one protein.
Reading frame: The reading frame describes how the proteins are divided into codons.
RNA polymerase: Enzyme used in transcribing mRNA.
Promoter: Sequence indicating the start of the template DNA strand for RNA polymerase.
tRNA: RNA that assists in translation by reading the mRNA strand and attaching the correct proteins.
Anticodon: The complementary codon carried on a tRNA that allows it to read the correct codon.
rRNA: RNA used in the structure of ribosomes.
Silent mutation: Mutation that results in no change of the final protein.
Missense mutation: Mutation that causes the encoding of a different protein than the one intended.
Nonsense mutation: Mutation that encodes for stop codon.
Substitution: Mutation that replaces a nucleotide pair with a different pair.
Insertion: Mutation that adds a nucleotide pair.
Deletion: Mutation that removes a nucleotide pair.
Frameshift mutation: when a mutation causes the RNA strand to be offset from the reading frame.
Mutagen: Substance that increases the odds of mutation.
Chapter 18
Bacteria: A type of single-celled prokaryotic organisms.
Operon: The operator, promoter and related genes.
Regulatory Gene: Gene that encodes for a repressor protein.
Epigenetic inheritance: Inheritance of traits transmitted by mechanisms outside of the nucleotide sequence.
Homeotic genes: regulatory genes that control pattern formation.
Chapter 19
Capsid: Protein shell enclosing the viral DNA.
Bacteriophage: Virus that infects bacteria.
Lytic cycle: Virus replication cycle that requires the death of the host.
Virulent phage : Phage that replicates only by the lytic cycle.
Lysogenic cycle: Virus replication cycle that does not require the death of the host.
Temperate phage: Phage capable of lytic and lysogenic cycles.
Restrictive enzymes: Enzymes in bacteria that restrict virus replication.
Viral envelope: Protective shell used by viruses to enter a host cell.