Difference between revisions of "Unit 2: The Cell"
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 184: | Line 184: | ||
# '''C4 plants: have an extra cell that other plants don't have (bundle sheath cells) where rubisco and CO2 can combine without oxygen''' | # '''C4 plants: have an extra cell that other plants don't have (bundle sheath cells) where rubisco and CO2 can combine without oxygen''' | ||
# '''CAM plants: take in carbon dioxide at night when stomata can be open''' | # '''CAM plants: take in carbon dioxide at night when stomata can be open''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Cell Communication == | ||
| + | Hormones: Molecules used for signalling | ||
| + | |||
| + | Ligand" Molecule that specifically binds to another. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Signal transduction pathway: A chain of interactions that can deliver a signal in the cell. | ||
| + | |||
| + | cAMP: Cyclic AMP. Signalling molecule that can be made from ATP | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Cell Cycle == | ||
| + | Cell division: One cell splitting into two new cells. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Genome: Genetic information of a cell. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Chromosome: Structures that make up DNA. | ||
| + | |||
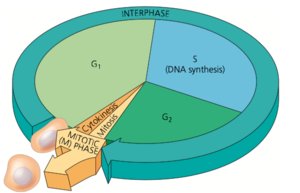
| + | Cell cycle: Composed of the mitotic phase, and the interphase. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Interphase: Composed of G1, S, and G2. About 90% of the full cell cycle. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Mitotic phase: Composed of mitosis and cytokinesis. About 10% of the full cell cycle. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Mitosis: Mitosis has five sub-stages. Prophase, pro-metaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Mitotic spindle: Structure made of microtubules. Pulls chromosomes apart into two separate chromatids. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Chromatid: Chromosomes are made of two chromatids. In mitosis, the chromatids are pulled apart and made into their own chromosomes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Uvavavl hxlkafdjvkladjfkajvajvlajflkvsd.png|thumb]] | ||
Latest revision as of 07:45, 22 February 2021
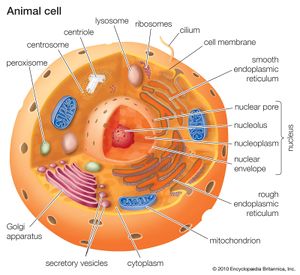
Nucleus: Stores DNA for the cell.
Eukaryotic cell: Has a nucleus, and lysosomes. Larger and more awesome than prokaryotic cells.
Prokaryotic cell: No nucleus. Small
Light microscope: uses lenses for focus.
Electron microscope: Creates beam of electrons for focus. It can be scanning, or transmission.
Cell fractionation: Taking a cell apart to study it.
see Lab techniques for more information.
Organelle: Component of a cell.
Mitochondrion: A organelle that makes ATP (a kind of chemical energy) for the cell. Has its own DNA.
Chloroplast: organelle in plant cells. Used for photosynthesis. Has its own DNA.
Rough endoplasmic reticulum: Organelle in a cell. Has lots of ribosomes on its surface, so it appears rough when looking at it through a microscope. Creates secretory proteins and membranes.
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum: Organelle in a cell. Does not have ribosomes on its surface, so it appears smooth when looking at it through a microscope. Used for metabolic processes.
Lysosome: Used to hydrolyse macromolecules. Has a different pH if it breaks open in a cell.
Vesicle: Transporter in the cell.
peroxisomes: Creates toxic hydrogen peroxide away from the rest of the cell. Fortunately it can also turn hydrogen peroxide back into water.
Cytoskeleton: skeleton for the cell. Also used in cell motility when it interacts with motor proteins.
Cell wall: Extracellular structure of plant cells.
Cytosol: Area of cell outside the nucleus.
Ribosome: Organelle that carry out protein synthesis.
Golgi apparatus: Ships and stores products of the endoplasmic reticulum out into the cell.
Cristae: Fold in mitochondria
Nucleolus: Mass of densely stained granules and fibres adjoining part of the chromatin.
Membrane structure and function
Diffusion: Substances move to areas with less concentration of itself.
Concentration gradient: The gradient of the concentration of a substance.
Integral proteins: Penetrate the hydrophobic interior of the lipid bilayer. Usually spans the full width of the membrane.
Peripheral proteins: Not embedded in the lipid bilayer. loosely bound to the membrane.
Transport protein: Protein in the membrane that moves substances out of the cell.
Osmosis: When water moves down its concentration gradient.
Osmoregulation: When a cell regulates water flowing in and out of itself.
Facilitated diffusion: when a substance is assisted in moving down its concentration gradient.
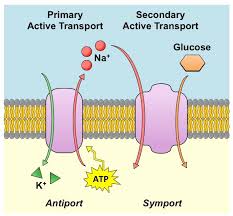
Active transport: When a substance is moved against its concentration gradient.
Electrochemical gradient: A substance's concentration gradient plus some electrical forces control the movement of the substance.
Cotransport: When a transport protein that uses the diffusion of one substance to power the active transport of another.
Exocytosis: The bulk transport of a large molecule from in the cell to out of the cell. A vesicle carries the molecule and then merges with the membrane. Releasing the molecule outside of the cell.
Endocytosis: When a pocket forms in the membrane to capture a substance and bring it back into the cell by turning into a vesicle. There are 3 types of endocytosis.
- Phagocytosis: A type of endocytosis. Where a cell "eats" a substance by engulfing it with pseudopodia.
- Pinocytosis: A type of endocytosis. Where a cell "drinks" substances by engulfing any substance it can capture.
- Receptor mediated endocytosis: A type of endocytosis. Where a cell "drinks" a specific substance by using receptors by the substance, and then engulfing those receptors.
Metabolism
Metabolic pathway: A series of reactions that turn a starting molecule into an end product.
Catabolic pathway: A metabolic pathway that releases energy by turning a starting molecule into a simpler one.
Anabolic pathway: A metabolic pathway that consumes energy to turn a starting molecule into a more complex one.
Kinetic energy: Energy associated with the relative movement of objects.
Thermal energy: Energy relating to the random movement of atoms and molecules.
Heat: Thermal energy in transport from one object to another.
Potential energy: The potential for energy that matter posses because of its location or structure.
Chemical energy: Type of potential energy that can be released in a chemical reaction.
First law of thermodynamics: Energy can never be created or destroyed.
Second law of thermodynamics: Every energy transfer or transformation causes an increase of entropy in the universe.
Entropy: Energy unavailable for use because it is not orderly.
Exergonic reaction: Reaction that releases energy into its surroundings.
Endergonic reaction: Reaction that absorbs energy from its surroundings.
Enzyme: Macromolecule that acts as a catalyst. Usually a protein.
Substrate: The reactant an enzyme acts on.
Active site: Site on an enzyme that a substrate binds with.
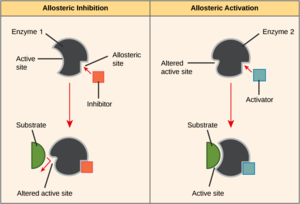
Competitive inhibitor: Reduces an enzyme's function by blocking its active site.
Non-competitive inhibitor: Reduces an enzyme's function by binding to a site that is not an active site.
Allosteric regulation: When a protein's function at one site is affected by a change at another site.
Allosteric activation and inhibition: A protein oscillates between an active and inactive state. And activator molecule stabilizes the protein in its active state. Whereas an inhibitor molecule stabilizes the protein in its inactive state.
Cooperative activation: When the binding of a substrate to a protein makes it easier for future substrates to bind to that protein.
Cellular Respiration
Oxidation: Loss of electrons.
Reduction: Gaining electrons. Yes, really: gaining.
Reducing agent: Substance that gives another an electron.
Oxidating agent: Substance that receives an electron.
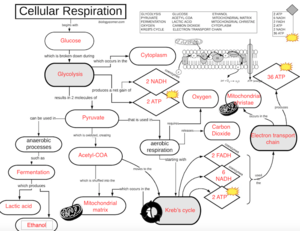
Aerobic respiration: Production of ATP that requires oxygen.
Anaerobic respiration: Production of ATP that does not require oxygen.
Glycolysis: The breakdown of glucose by enzymes. Releases pyruvate. Happens in the cytoplasm. Step 1
Pyruvate: created by Glycolysis. Used in fermentation and the Kreb's cycle.
Kreb's cycle: Cycle involved in cellular respiration. Also know as the citric acid cycle. Invented by someone with the last name Krebs. Step 2
Is this perhaps where Carbon dioxide is formed? where does it happen?
Electron transport train: Used in cellular respiration. Consumes 2 ATP, and produces 2 FADH into 36 ATP. Step 3
CHEMIOSMOSIS = Ions going across a membrane.
OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION = Adds a phosphate group to a molecule.
ATP SYNTHASE = Catalyst enzyme for ATP.
Fermentation: Used in anaerobic respiration. There are tow types of fermentation: lactic acid fermentation , and alcohol fermentation.
Lactic acid: produced by fermentation.
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis: Synthesis using light. Occurs in plants.
Stroma: Dense fluid inside chloroplast. If the cell loses too much water they must close.
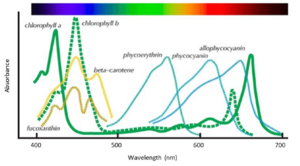
Pigment: Substance that absorbs visible light. Chlorophyll is a pigment.
Spectrophotometry: Measurement of the reflection or transmission properties of a material related to its wavelength. Lab techniques
Absorption spectrum: A graph plotting a pigment’s light absorption compared with its wavelength.
Light reactions: Process that occurs in chloroplasts. Takes in light and releases o2 and ATP. Occurs in the thylakoids.
Calvin cycle: Process that occurs in chloroplasts. Takes in co2 and produces glucose. Occurs in the Stroma.
C3 PLANTS = Uses the Calvin cycle for photosynthesis.
PHOTORESPIRATION = when a plant must use rubisco to oxidise rubp instead of carbon dioxide. This technique is generally considered very inefficient, and is probably a relic of evolution. Some plants capture carbon dioxide to avoid photorespiration. Not exactly...in regular C3 plants, rubisco binds Carbon dioxide to RuBP UNLESS there's Oxygen. For the most part there isn't oxygen because oxygen is being released. But when the stomata are closed (let's say there's a drought), oxygen is not being released and extra carbon dioxide isn't coming in. So now, rubisco prefers oxygen and starts photorespiration (takes up ATP and produces CO2).
There are 2 mechanisms that plants have come up with:
- C4 plants: have an extra cell that other plants don't have (bundle sheath cells) where rubisco and CO2 can combine without oxygen
- CAM plants: take in carbon dioxide at night when stomata can be open
Cell Communication
Hormones: Molecules used for signalling
Ligand" Molecule that specifically binds to another.
Signal transduction pathway: A chain of interactions that can deliver a signal in the cell.
cAMP: Cyclic AMP. Signalling molecule that can be made from ATP
Cell Cycle
Cell division: One cell splitting into two new cells.
Genome: Genetic information of a cell.
Chromosome: Structures that make up DNA.
Cell cycle: Composed of the mitotic phase, and the interphase.
Interphase: Composed of G1, S, and G2. About 90% of the full cell cycle.
Mitotic phase: Composed of mitosis and cytokinesis. About 10% of the full cell cycle.
Mitosis: Mitosis has five sub-stages. Prophase, pro-metaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Mitotic spindle: Structure made of microtubules. Pulls chromosomes apart into two separate chromatids.
Chromatid: Chromosomes are made of two chromatids. In mitosis, the chromatids are pulled apart and made into their own chromosomes.